CloudFront
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- CloudFront Core Components
- CloudFront Distributions
- Lambda@Edge
- CloudFront Protection
- Caching Policy
- Caching Behaviors
- Geo-Restriction
- CloudFront Signed URL
- Pricing
Introduction
- Content Distribution Network (CDN) creates cached copies of your website at various Edge locations around the world
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- A CDN is a distributed network of servers which delivers web pages and content to users based on their geographical location, the origin of the webpage and a content delivery server
- Can be used to deliver an entire website including static, dynamic and streaming
- 216 points of presence globally
- DDoS protection since it is a global service. Integrates with AWS Shield and AWS WAF
- Requests for content are served from the nearest Edge Location for the best possible performance
- A CDN is a distributed network of servers which delivers web pages and content to users based on their geographical location, the origin of the webpage and a content delivery server
CloudFront Core Components
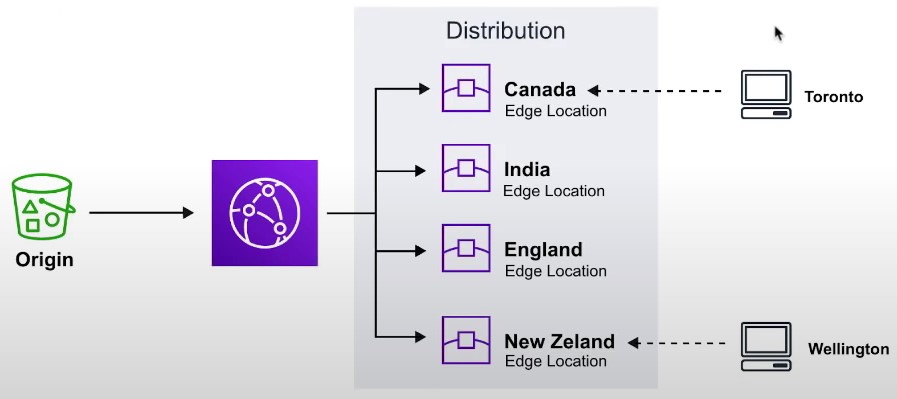
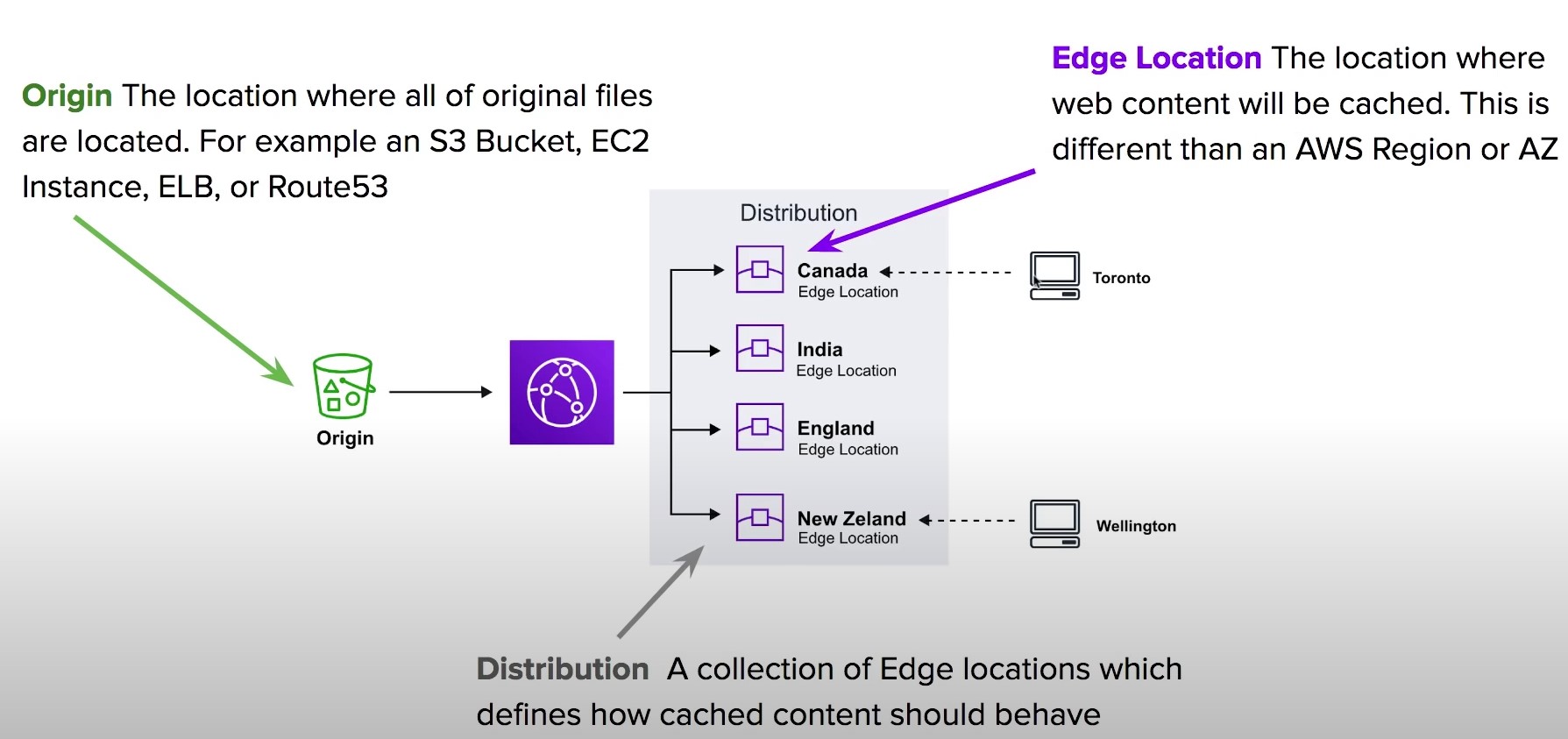
- Origin
- The location where all of original files are located. For example an S3 Bucket, EC2 Instance, ELB or Route53
- Edge Location
- The location where web content will be cached. This is different than an AWS Region or AZ
- Distribution
- A collection of Edge locations which defines how cached content should behave
- A collection of Edge locations which defines how cached content should behave
CloudFront Distributions
- A distribution is a collection of Edge Location. You specific the Origin eg. S3, EC2, ELB, Route53
- It replicates copies based on your Price Class
- There are two types of Distributions
- Web (for Websites)
- RTMP (for streaming media)
- Behaviors
- Redirect to HTTPs, Restrict HTTP Methods, Restrict Viewer Access, Set TTLs
- Invalidations
- You can manually invalidate cache on specific files via Invalidations
- Error Pages
- You can serve up custom error pages eg 404
- Restrictions
- You can use Geo Restriction to blacklist or whitelist specific countries
Lambda@Edge
-
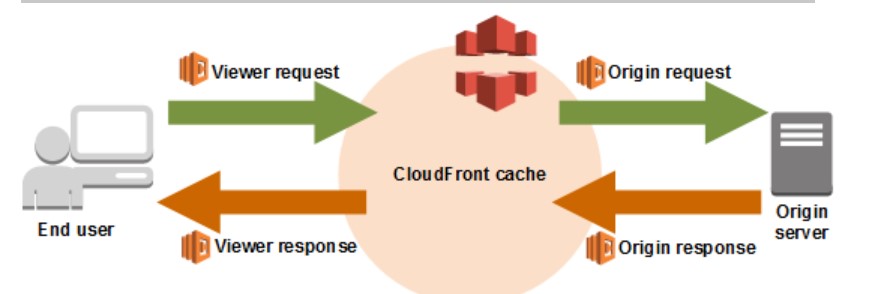
Lambda@Edge functions are used to override the behavior of request and responses
-
Lambda@Edge lets you run Lambda functions to customize the content that CloudFront delivers, executing the functions in AWS locations closer to the viewer.
-
The functions run in response to CloudFront events, without provisioning or managing servers. You can use Lambda functions to change CloudFront requests and responses at the following points:
-
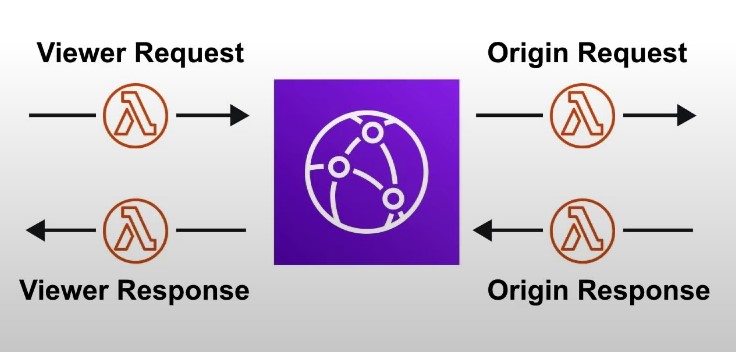
The 4 Available Edge Functions
- Viewer Request
- When CloudFront receives a request from a Viewer
- Origin request
- Before CLoudFront forwards a request to the origin
- Origin response
- When cloudfront receives a response from the origin
- Viewer response
- Before CLoudFront returns the response to the viewer
- Viewer Request
CloudFront Protection
- By Default a Distribution allows everyone to have access
- Original Identity Access (OAI)
- A virtual user identity that will be used to give your CloudFront Distribution permission to fetch a private object
- Inorder to use Signed URLs or Signed Cookies you need to have an OAI
- Signed URLs
- (Not the same thing as S3 Presigned URL)
- A url with provides temporary access to cached objects
- (Not the same thing as S3 Presigned URL)
- Signed Cookies
- A cookie which is passed along with the request to CloudFront. The advantage of using a Cookie is you want to provide access to multiple restricted files. eg. Video Streaming
Caching Policy
- Each object in the cache will be identified by a cache key
- Maximize the cache-hit-ratio by minimizing requests to the origin
- Cache Key
- a unique identifier for everything in the cache
- by default, made up of the hostname and resource portion of the URL
- The cache key can be customized by creating a CloudFront Cache Policy
Caching Behaviors
- Configure different settings for a given URL path pattern
- Example: configure a specific behavior for requests to /images/*.jpg
- Route to different kinds of origins/origin groups based on the content-type or path.
- Examples:
- /images/* to S3
- /login to EC2
- /api to API Gateway
Geo-Restriction
- Restrict who can access your CloudFront distribution based on the country where the distribution was access from
- You can create an AllowList or a BlockList
CloudFront Signed URL
- Two types of signers:
- Either a trusted key group (Recommended)
- An AWS Account that contains a CloudFront Key Pair
- In your distribution, create one or more trusted key groups
Pricing
- You can reduce the number of edge locations for a cost savings
- Price Classes
- Price Class All: All regions, best performance
- Price Class 200: most regions, but excludes the most expensive regions
- Price Class 100: only the least expensive regions