Elastic Load Balancer
- Spread load of traffic across multiple downstream instances
-
Health check downstream instances
- SSL Termination
- High Availability across zones
- Add backend instances to a “Target Group”
Types of ELB
-
Application Load Balancer (Layer 7)
- Allows you to route to multiple instances in a Target Group (aka Backend Pool in Azure)
- Supports HTTP/2 and websocket
- Route based on the path in the URL, hostname, query strings, and headers
- Extra headers added by ALB
- x-forwarded-for
- x-forwarded-proto
- x-forwarded-port
- ALB has a WAF capability that can be enabled
-
Network Load Balancer (Layer 4)
- High performance, millions of requests per second, and less latency ~100 ms
- NLB has one static IP address per AZ, and supports assigning an Elastic IP
- Not compatibly with the free tier
-
Gateway Load Balancer (Layer 3)
- Use cases: Send all traffic to a firewall, IDS, IPS, etc.
- Supports the GENEVE protocol on port udp/6081
Sticky Sessions
- Same client is forwarded to the same instance, rather than spreading traffic amongst all instances
- Supported by the ALB and NLB
- Cookie is set on the client with has an expiration date you control
- Cookies:
- Two types of cookie are supported:
- Application Based Cookie:
- Custom cookie:
- Generated by the target
- Can include any custom attributes required by the application
- The cookie name must be specified individually per target group
- You cannot use AWSALB, AWSALBAPP, or AWSALBTG. These are all reserved by AWS
- Application Cookie:
- Generated by the LB itself
- Cookie will be AWSALBAPP
- Custom cookie:
- Duration-based Cookie
- Cookie is generated by the load balancer itself
- Cookie name is AWSALB for ALB
- Application Based Cookie:
- Two types of cookie are supported:
- Cookies:
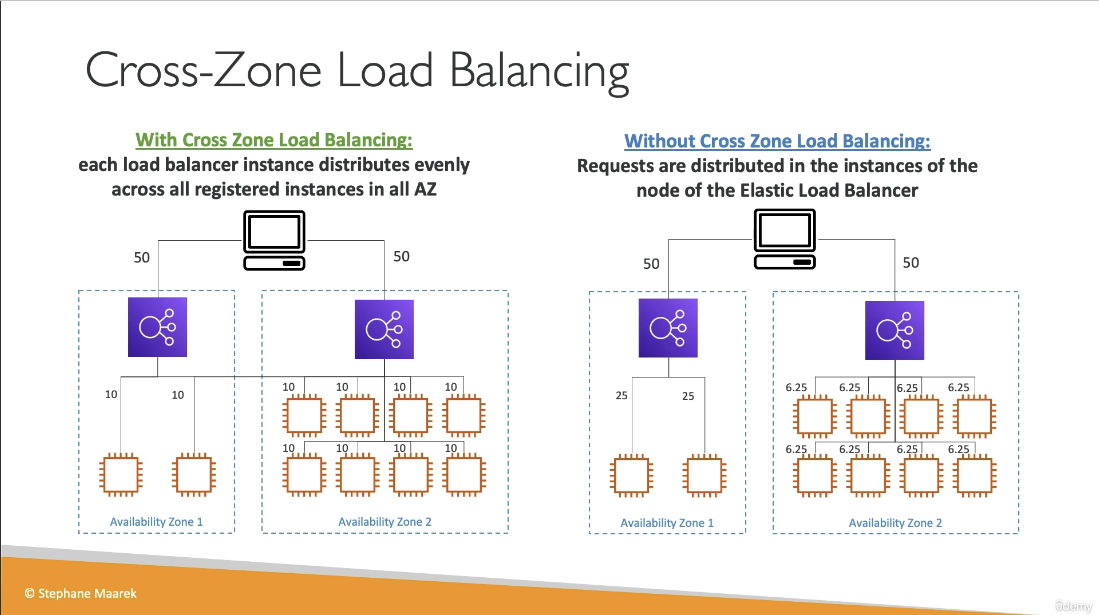
Cross-Zone Load Balancing
- Each load balancer instance distributes traffic evenly across all registered instances in all AZ
- For the ALB, cross-zone load balancing can be enabled/disabled at the target group level. It is enabled by default and there are no additional charges
- Can be enabled for NLB and GLB, but additional charges will apply. It is disabled by default.
SNI
- Works with ALB, NLB, and CloudFront
Deregistration Delay
- AKA Connection Draining
- Stop sending new requests to the instance that is being deregistered
- Allows the instance to complete in-flight requests before being terminated
- 1 to 3600 seconds (default 300 seconds)
- Can be disabled (set to 0 seconds)
- Set to a low value if your requests are short-lived