Route53
Introduction
- A highly available, fully managed, scalable, authoritative DNS service provided by Amazon
- Also a domain registrar
- Supports health checks for resources registered with DNS names
- The only AWS service that provides 100% availability
Hosted Zones
- Public Hosted Zones
- contains records that specify how to route traffic on the internet
- Private Hosted Zones
- Only hosts within the VPC can resolve the DNS names
- You will pay 50 cents per month for each hosted zone
- Domain names will cost you $12/year
TTL
- Time to live
- i.e. how long a DNS record will be cached on a client machine
CNAME vs Alias
- lb l-1234.us-east-2.elb.amazonaws.com and you want myapp.mydomain.com
- CNAME:
- Points a hostname to any other hostname (app.domain.com => blabla.anything.com)
- You cannot create a CNAME for the Apex record (root domain)
- Alias:
- Points a hostname to an AWS Resource (app.mydomain.com => blabla.amazonaws.com)
- WORKS for ROOT DOMAIN and NON ROOT DOMAIN (aka, mydomain.com)
- Free of charge
- Native health check
- Only supported for A and AAAA record types
- Cannot set alias for an EC2 instance name
Routing Policies
-
Simple
- Typically, the simple type of routing policy will resolve to a single resource
- If the record resolves to multiple values, the client will choose a random one
- When using the Alias record type, the record can only resolve to one resource
-
Weighted
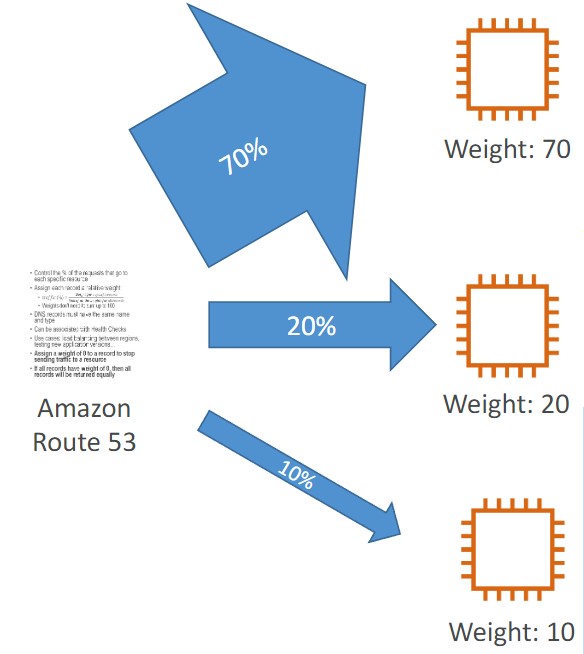
- Control the % of the requests that go to each specific resource.
- Assign each record a relative weight
- $ \text traffic {(%)} = {\displaystyle \text {weight for a specific record } \over \displaystyle \text {sum of all the weights for all records }} $
- The sum of the weights of all records does not need to equal 100
- DNS records must have the same name and type
- Can be associated with Health Checks
- Use cases: load balancing between regions, testing new application versions
-
Latency
- Redirect to the resource that has the least latency close to us
- Super helpful when latency for users is a priority
- Latency is based on traffic between users and AWS Regions
- Germany users may be directed to the US (if that’s the lowest latency)
- Can be associated with Health Checks (has a failover capability)
-
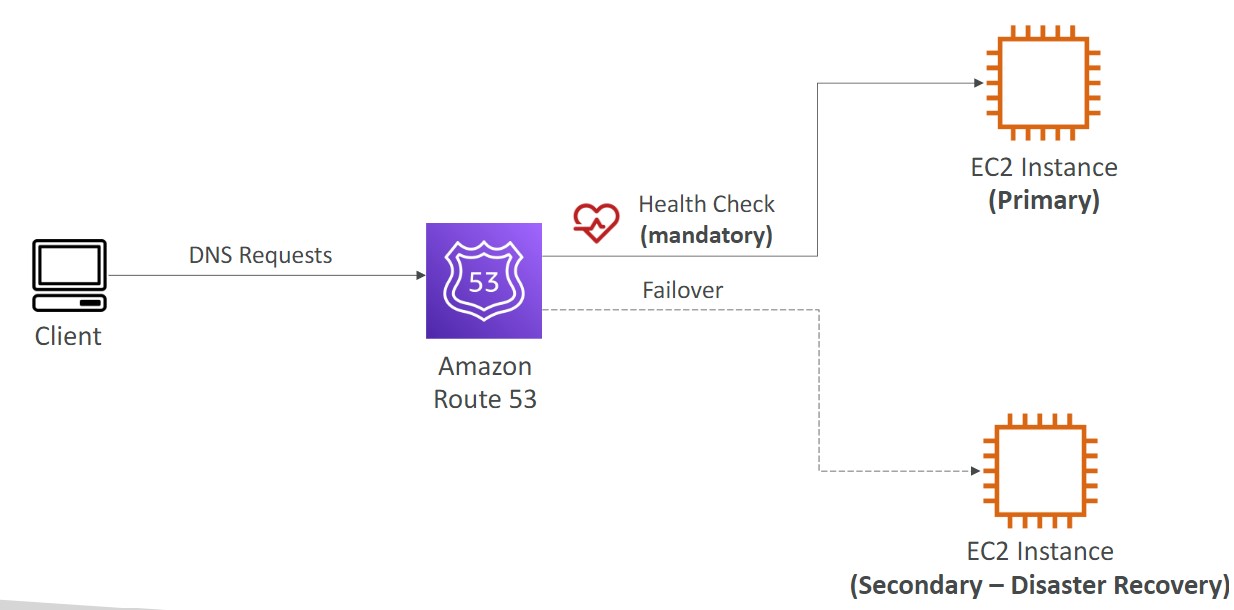
Failover
-
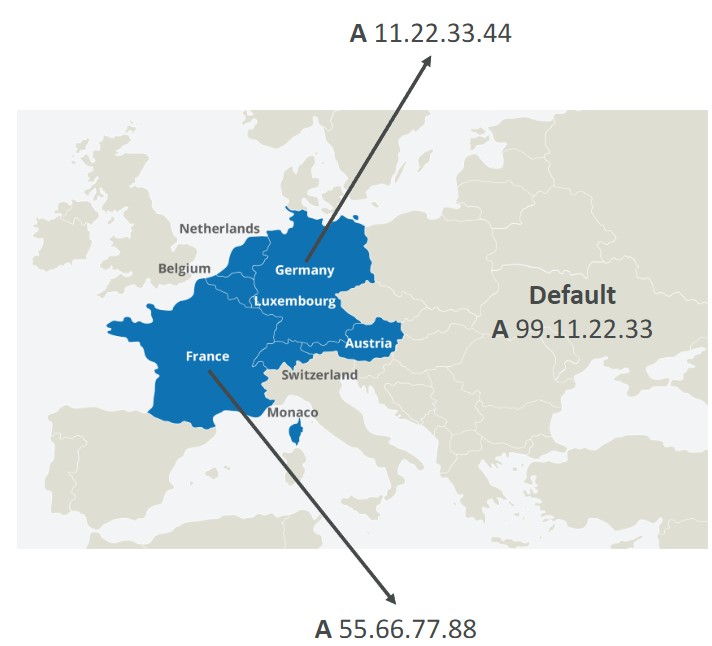
Geolocation
- Different from latency based
- This routing is based on user location
- Should create a “Default” record (in case there’s no match on location)
- Use cases: website localization, restrict content distribution, load balancing
- Can be associated with Health Checks
-
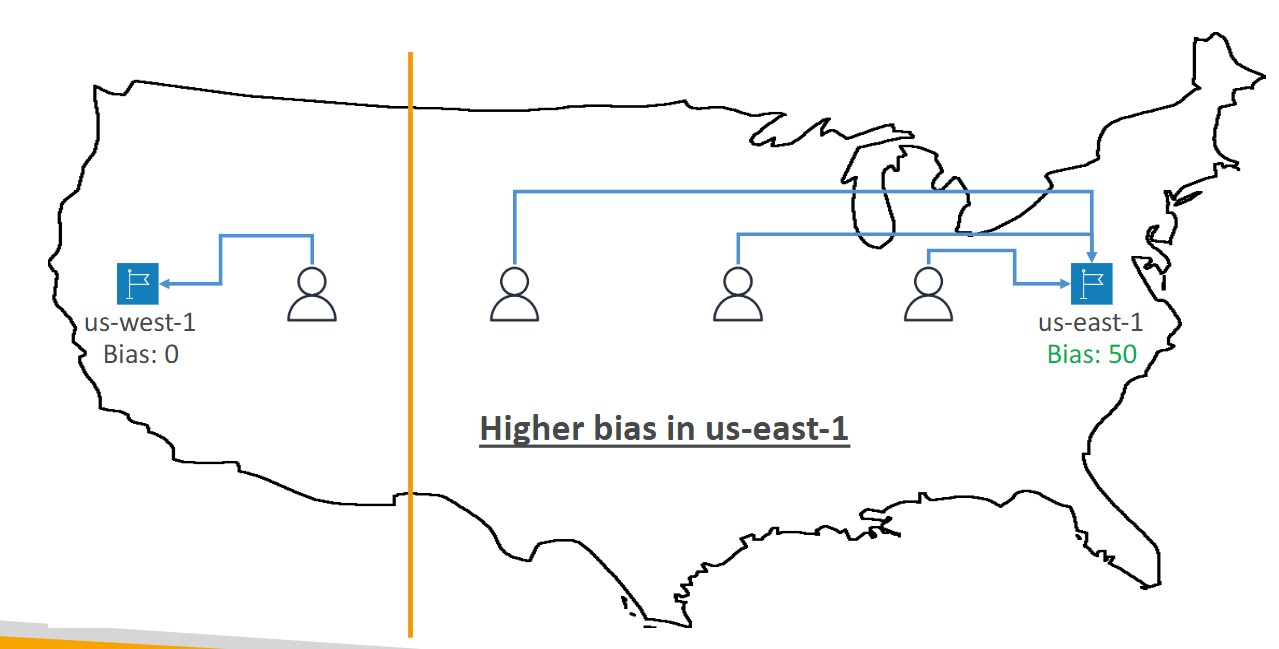
Geoproximity
- Route traffic to your resources based on the location of users and resources
- Ability to shift more traffic to resources based on the defined bias
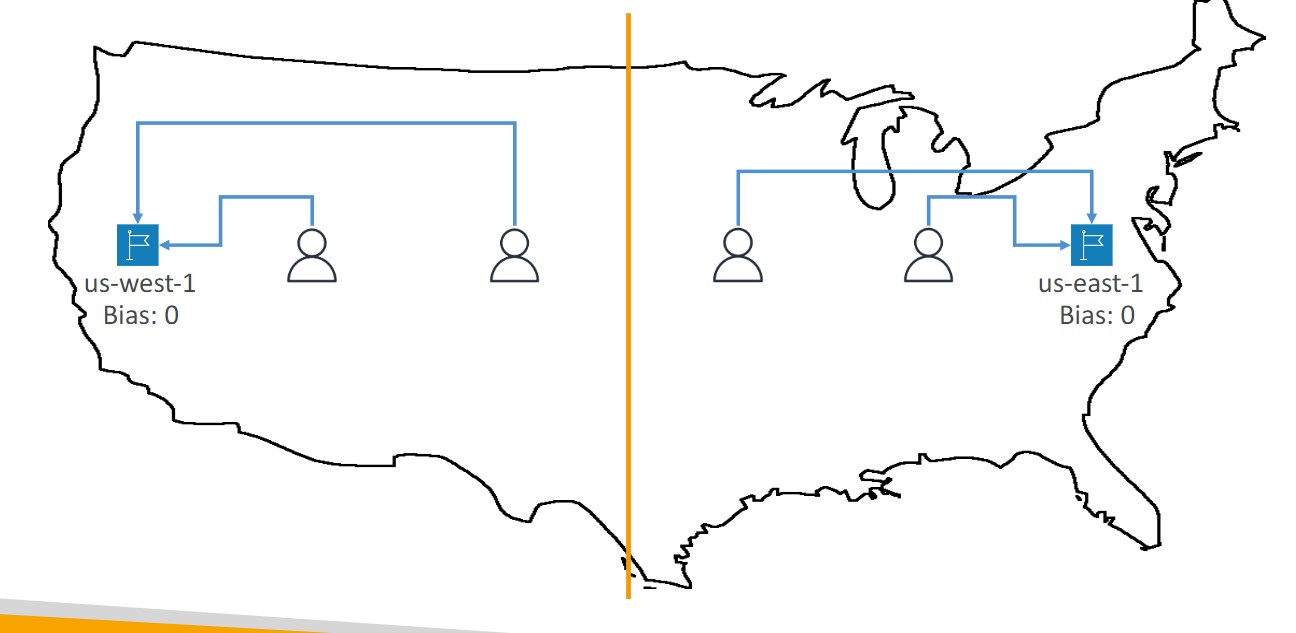
- To change the size of the geographic region, specify bias values:
- To expand (1 to 99)- more traffic to the resource
- To shrink (-1 to 99)- less traffic to the resource
- Resources can be:
- AWS resources (specify AWS region)
- Non-AWS resources (specify Latitude and Longitude)
- You must use Route 53 Traffic Flow to use this feature
-
Health Checks
- HTTP Health Checks are only for public resources. You must create a CloudWatch Metric and associate a CloudWatch Alarm, then create a Health Check that checks the alarm
- 15 global health checkers
- Health checks methods:
- Monitor an endpoint
- Healthy/unhealthy threshold - 3 (default)
- Interval 30 seconds
- Supports HTTP, HTTPS, and TCP
- if > 18% of health checkers report the endpoint is healthy, Route53 considers it healthy.
- You can choose which locations you want Route53 to use
- You must configure the firewall to allow traffic from the health checkers
- Calculated Health Checks
- Combine the results of multiple health checks into a single health check
- Monitor an endpoint
Configuring Amazon Route 53 to route traffic to an S3 Bucket
- An S3 bucket that is configured to host a static website
- You can route traffic for a domain and its subdomains, such as example.com and www.example.com to a single bucket.
- Choose the bucket that has the same name that you specified for Record name
- The name of the bucket is the same as the name of the record that you are creating
- The bucket is configured as a website endpoint