S3
Introduction
- Storage
- Files are stored in Buckets, the files are called objects
- Storage Accounts must have a globally unique DNS name
- Buckets are regional
- Bucket names must have no uppercase, no underscore, 3-63 characters long, not an IP address, must start with a lowercase letter or number
- Objects (files) have a key, which is the FULL path of the object:
- Example of a prefix
- bucket/folder1/subfolder1/mypic.jpg => prefix is /folder1/subfolder1/
- Example of a prefix
- S3 Select
- Use SQL like language to only retrieve the data you need from S3 using server-side filtering
- Max object size is 5TB
- If you upload a file larger than 5GB, you must use Multi-part Upload
- Objects can have metadata
S3 Security
-
User-Based
- IAM Policies - Which API calls are allowed for an IAM user
-
Resource-Based
- Bucket Policies- bucket wide rules form the S3 Console - allows cross account
- Object ACL - Finer grained (can be disabled)
- Bucket ACL - less common (can be disabled)
-
An IAM Principal can access an S3 object if:
- The user IAM permissions ALLOW it OR the resource policy allows it and there is no explicit Deny
-
Bucket Policies - Bucket wide rules from the S3 console
-
JSON based policy
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [{ "Sid": "AllowGetObject", "Principal": { "AWS": "*" }, "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "s3:GetObject", "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET/*", "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "aws:PrincipalOrgID": ["o-aa111bb222"] } } }] } -
You can use the AWS Policy Generator to create JSON policies
-
S3 Static Website Hosting
- You must enable public reads on the bucket
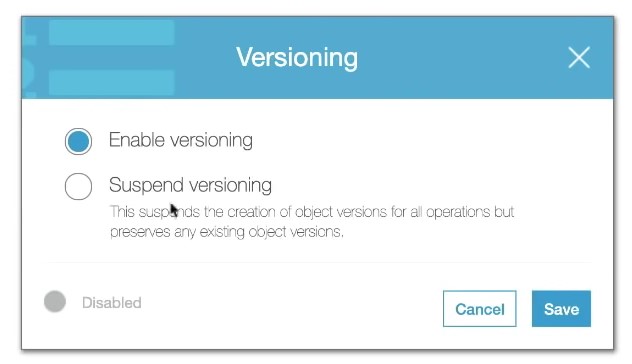
S3 Versioning
-
allows to version the object
-
Stores all versions of an object in S3
-
Once enabled it cannot be disabled, only suspended on the bucket
-
Fully integrates with S3 Lifecycle rules
-
MFA Delete feature provides extra protection against deletion of your data
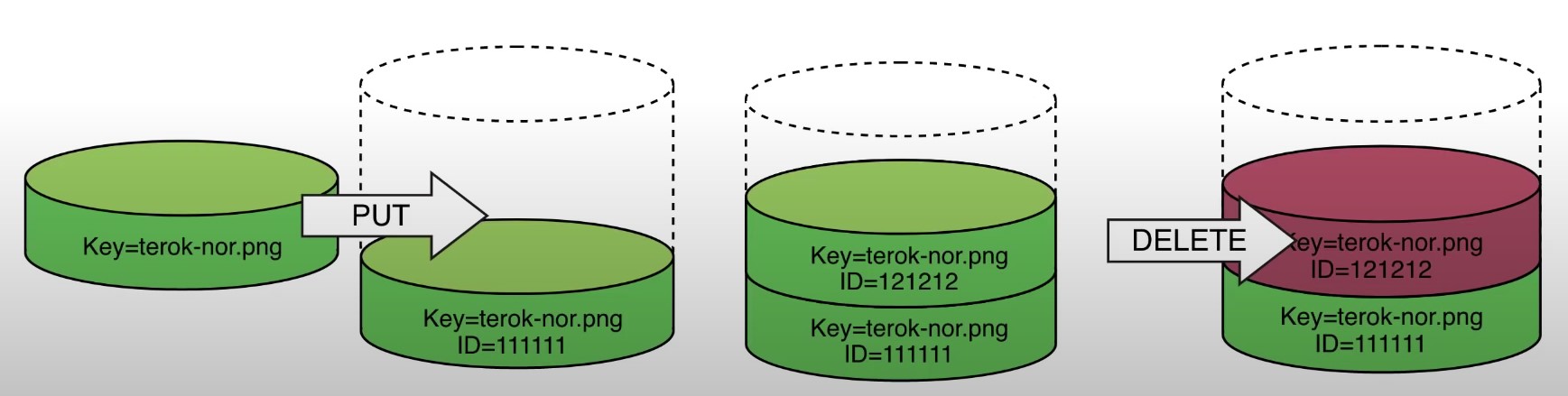
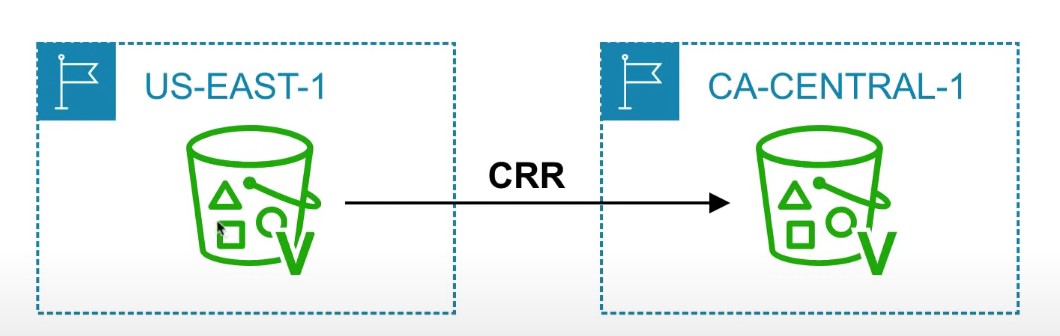
S3 Cross-Region Replication or Same-Region Replication
-
When enabled, any object that is uploaded will be Automatically replicate to another region or from source to destination buckets
-
Must have versioning turned on both the source and destination buckets.
-
Can have CRR replicate to another AWS account
-
Replicate objects within the same region
-
You must give proper IAM permissions to S3
-
Buckets can be in different AWS accounts
-
Only new objects are replicated after enabling replication. To replicate existing objects, you must use S3 Batch Replication
-
For DELETE operations, you can optionally replicate delete markers. Delete Markers are not replicated by default.
-
To replicate, you create a replication rule in the “Management” tab of the S3 bucket. You can choose to replicate all objects in the bucket, or create a rule scope
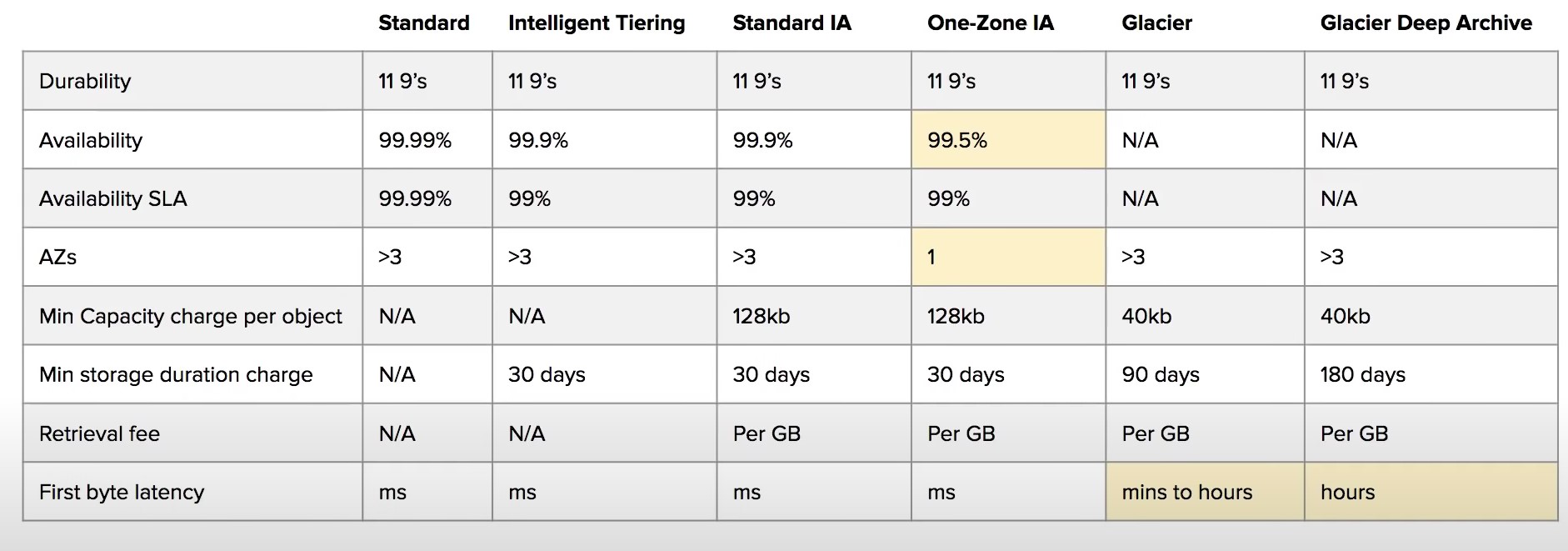
S3 Storage Classes
- AWS offers a range of S3 Storage classes that trade Retrieval, Time, Accessability and Durability for Cheaper Storage
(Descending from expensive to cheaper)

-
S3 Standard (default)
- Fast! 99.99 % Availability,
- 11 9’s Durability. If you store 10,000,000 objects on S3, you can expect to lose a single object once every 10,000 years
- Replicated across at least three AZs
- S3 standard can sustain 2 concurrent facility failures
-
S3 Intelligent Tiering
- Uses ML to analyze object usage and determine the appropriate storage class
- Data is moved to most cost-effective tier without any performance impact or added overhead
-
S3 Standard-IA (Infrequent Access)
- Still Fast! Cheaper if you access files less than once a month
- Additional retrieval fee is applied. 50% less than standard (reduced availability)
- 99.9% Availability
-
S3 One-Zone-IA
- Still fast! Objects only exist in one AZ.
- Availability (is 99.5%). but cheaper than Standard IA by 20% less
- reduces durability
- Data could be destroyed
- Retrieval fee is applied
-
S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval
- Millisecond retrieval, great for data accessed once a quarter
- Minimum storage duration of 90 days
-
S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval
- data retrieval: Expedited (1 to 5 minutes), Standard (3 to 5 hours), Bulk (5 to 12 hours) - free
- minimum storage duration is 90 days
- Retrieval of data can take minutes to hours but the off is very cheap storage
-
S3 Glacier Deep Archive
- The lowest cost storage class - Data retrieval time is 12 hours
- standard (12 hours), bulk (48 hours)
- Minimum storage duration is 180 days
-
S3 Glacier Intelligent Tiering
-
Storage class comparison
-
S3 Guarantees:
- Platform is built for 99.99% availability
- Amazon guarantee 99.99% availability
- Amazon guarantees 11’9s of durability
S3 LifeCycle Rules
- Types of rules:
- Transition Actions
- Move objects between storage classes automatically
- Expiration Actions
- Configure objects to expire (delete) after some time
- Can be used to delete incomplete multi-part uploads
- Delete access logs automatically
- Can be used to delete old versions of files if versioning is enabled
- Transition Actions
- Rules can be specified for objects with a certain prefix or tag
Event Notifications
- Examples of events:
- S3:ObjectCreated, S3:ObjectRemoved, S3:ObjectRestore
- Object name filtering is possible (*.jpg for example)
- Send a notification when an event occurs
- Uses SNS, Lambda, or SQS to send the notifications to
- Requires a SNS Resource Policy, SQS Resource Policy, or a Lambda Resource Policy allowing S3 bucket to write to the resource
- You can also send events to EventBridge, which can then be used to send the events to 18 other AWS services
S3 Encryption
- 4 types of encryption in S3
- Server side encryption with managed keys (SSE-S3)
- Key is completely managed by AWS, you never see it
- Object is encrypted server-side
- Enabled by default
- Uses AES-256, must set header
"x-amz-server-side-encryption": "AES256"
- Uses AES-256, must set header
- Server side encryption with KMS keys stored in AWS KMS (SSE-KMS)
- Manage the key yourself, store the key in KMS
- You can audit the key use in CloudTrail
- Uses AES-256, must set header
"x-amz-server-side-encryption": "AWS:KMS"
- Uses AES-256, must set header
- Accessing the key counts toward your KMS Requests quota (5500, 10000, 30000 rps, based on region)
- You can request a quota increase from AWS
- Server Side Encryption with customer provided keys (SSE-C)
- Can only be enabled/disabled from the AWS CLI
- AWS doesn’t store the encryption key you provide
- The key must be passed as part of the headers with every request you make
- HTTPS must be used
- CSE (Client side encryption)
- Clients encrypt/decrypt all the data before sending any data to S3
- Customer fully managed the keys and encryption lifecycle
- Server side encryption with managed keys (SSE-S3)
- Encryption in Transit
- Traffic between local host and S3 is achieved via SSL/TLS
MFA Delete
- MFA Delete ensures users cannot delete objects from a bucket unless they provide their MFA code.

- MFA delete can only be enabled under these conditions
- The AWS CLI must be used to turn on MFA delete
- The bucket must have versioning enabled
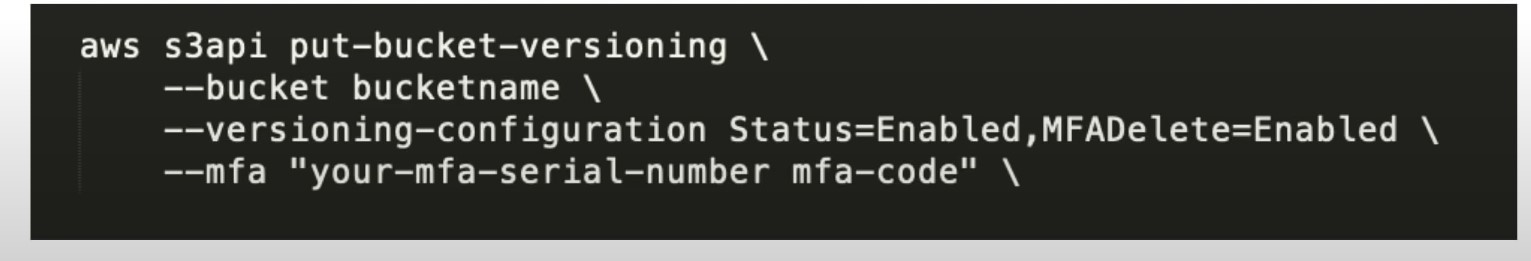
- Only the bucket owner logged in as Root User can DELETE objects from bucket
Presigned URLs
-
Generates a URL which provides temporary access to an object to either upload or download object data.
-
The pre-signed URL inherites the permission of the user that created the pre-signed URL
-
Presigned Urls are commonly used to provide access to private objects
-
Can use AWS CLI or AWS SDK to generate Presigned Urls

-
If in case a web-application which need to allow users to download files from a password protected part of the web-app. Then the web-app generates presigned url which expires after 5 seconds. The user downloads the file.