Disaster Recovery
-
RPO: how much data loss are you willing to accept during a disaster
-
RTO: how much downtime can you accept
Disaster Recovery in AWS
-
Any event that has a negative impact on a company’s business continuity or finances is a disaster
-
Disaster recovery (DR) is about preparing for and recovering from a disaster
-
What kind of disaster recovery?
- On-premise => On-Premise: traditional DR and very expensive
- On-Premise => AWS cloud: hybrid recovery
- AWS Cloud Region A => AWS Cloud Region B
-
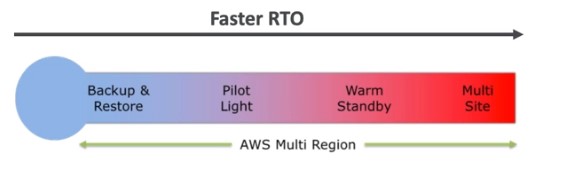
Disaster Recovery Strategies
-
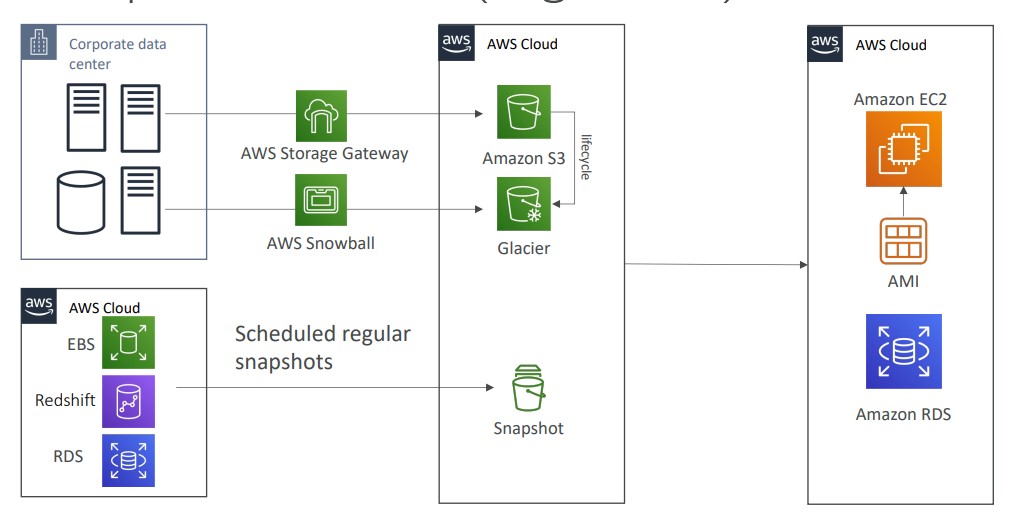
Backup and Restore
-
High RPO
-
Cheap
-
Easy to implement
-
-
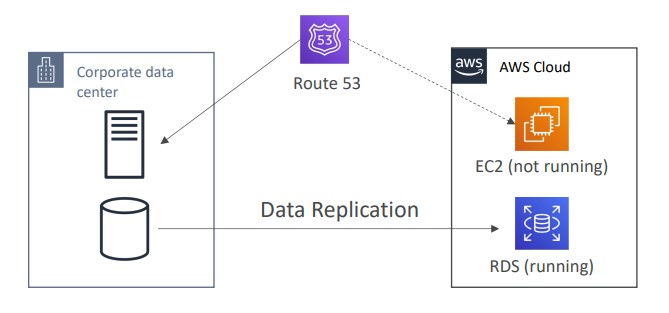
Pilot Light
- small version of the app is always running in the cloud
- Useful for the critical core components of the application (Pilot Light)
- Very similar to Backup and Restore
- Faster than Backup and Restore as critical systems are already up
-
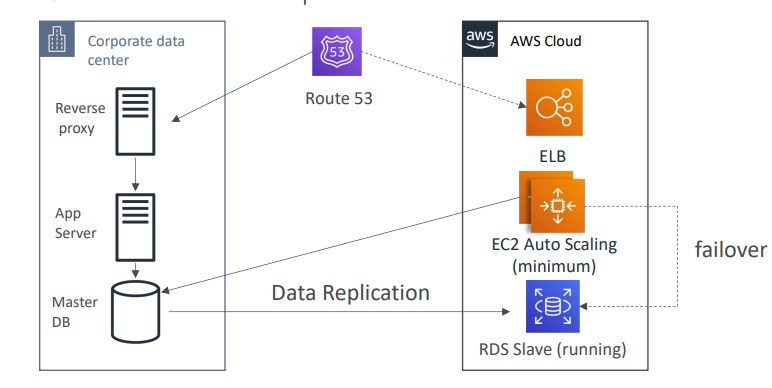
Warm Standby
- Full system is up and running, but at minimum size
- Upon disaster we can scale to production load
-
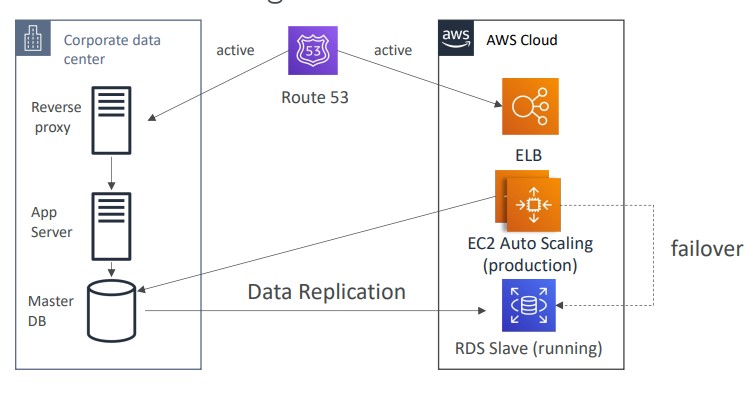
Hot Site/ Multi Site Approach
- Very low RTO (minutes or seconds) - very expensive
- Full production scale is running AWS and On Premise
-
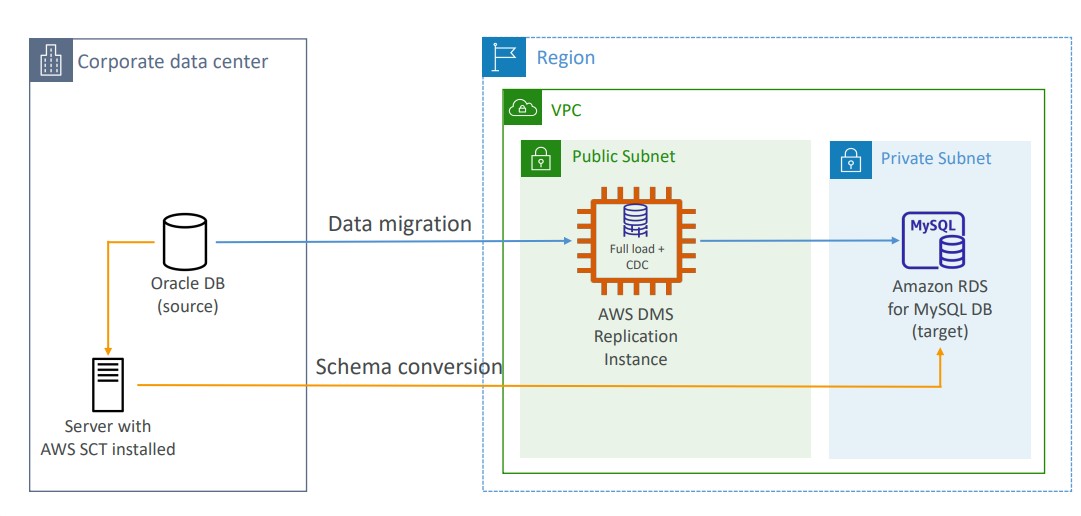
Database Migration Service
- Supports heterogeneous and homogeneous migrations
- You must create an EC2 instance to perform the replication tasks
- Sources can be on-prem databases or EC2-based databases, Azure SQL Databases, Amazon RDS, Amazon S3, and DocumentDB
- Targets can be on-prem databases, Amazon RDS, Redshift, DynamoDB, OpenSearch, Redis, Babelfish, DocumentDB, etc.
- AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) can convert the database schema from one engine to another if you are migrating to a different database engine
Continuous Replication
Multi-AZ Deployment
- When Multi-AZ Enabled, DMS provisions and maintains a synchronously stand replica in a different AZ
- Advantages:
- Provide Data Redundancy
- Eliminates I/O freezes
- Minimizes latency spikes
- Advantages:
RDS to Aurora Migration
- Options:
- Snapshot RDS and migrate to Aurora
- Create an Aurora Read REplica from RDS mySQL and when the replication lag is 0, promote it as it’s own DB Cluster
- If MySQL is external to RDS, you can backup with Percona XtraBackup and import into Aurora
- Use DMS if both databases are up and running
On-premise Strategies
- You can download Amazon Linux ISO and run on-prem hypervisors
- Import/export VMs for on-prem to AWS
- Use AWS Application Discovery Service to gather info about on-prem VMs and plan a migration
- Track with AWS migration hub
- Agentless Discovery
- VM inventory, configuration, performance history, etc.
- Agent-Based Discovery
- System configuration, system performance history, running processes, network connection details, etc.
- Use Application Migration Service (MGN) to lift-and-shift VMs to AWS
- AWS Database Migration Service
- Migrate data across database engines
- Migrate databases from on-prem to AWS
- AWS Server Migration
- Incremental replication of on-prem servers to AWS
- Converts on-prem servers to cloud-based servers
AWS Backup#
- Fully managed
- Centrally manage and automate backups across all AWS services
- AWS Backup supports cross-region backups and cross-account backups
- Backup policies are known as Backup Plans
- Vault Lock is used to enforce a Write-Once-Read-Many policy (WORM) to ensure backups in the Vault cannot be deleted. Even the root user cannot delete backups when enabled.