- What is Database
- What is Data Warehouse
- What is a key value store?
- What is a document database?
- NOSQL Database Services
- Relational Database Service
- Other Database Services
What is Database ?
- A database is data-store that store semi-structured and structured data
- A database is more complex stores because it requires using formal design and modeling techniques
- Database types:
- Relational Database
- Structured data represents tabular data (tables,rows and columns)
- Non-Relational Database
- Semi-Structured that may or may not represent tabular data
- Relational Database
- Set of functionality:
- query
- modeling strategies to optimize retrieval for different use cases
- control over the transformation of the data into useful data structures or reports
What is Data Warehouse ?
- Relational Database : designed for analytic workloads and a column-oriented data-store
- Companies will have terabytes and millions of rows of data
- Data warehouses generally perform aggregation
- aggregation is is grouping data eg. finding a total or average
- Data warehouses are optimised around columns since they need quickly aggregate column data
- Data warehouses are generally designed be HOT
- HOT means they can return queries very fast even though they have vast amounts of data
- Data warehouses are infrequently accessed
- intended for real time reporting but maybe once or twice a day or once a week to generate business or user reports
- Data Warehouse needs to consume data from a relational database on a regular basis
What is a Key Value Store ?
- A key-value database is a type of non-relational database (NoSQL) that uses a simple key-value method to store data
- Stores a unique key alongside a value
- will interpret this data resembling a dictionary
- can resemble tabular data, it does not have to have the consistent columns per row -Due to simple design so they can scale well beyond a relational database
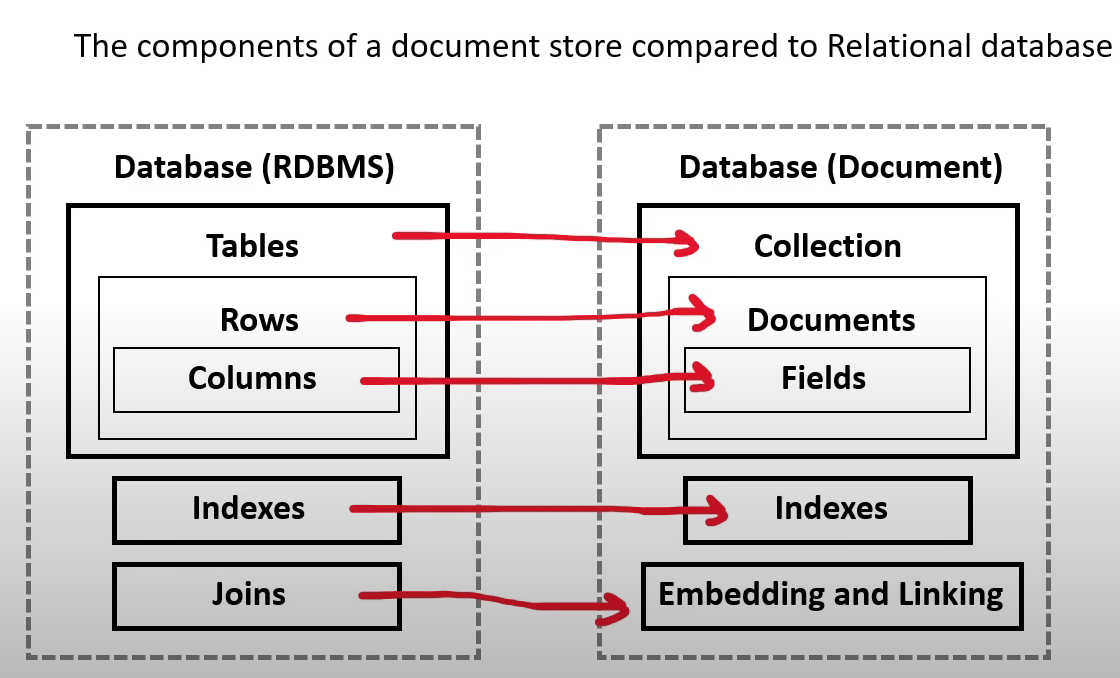
What is a document database ?
- Document store
- a NOSQL database that stores documents as its primary data-structure
-
it could be an XML but more commonly is JSON or JSON-like
-
they are sub-class of key/value stores
-
NOSQL Database Services
-
DynamoDB
- a serverless NOSQL key/Value and document database
- designed to scale to billions of records with consistent data return in at least a second- millisecond latency
- It is AWS’s flagship database service meaning it is cost-effective and very fast
- DAX cluster for read cache, microsecond read latency
- Event Processing: DynamoDB Streams to integrate with AWS Lambda, or Kinesis Data Streams
- Global Table feature: active-active setup
- Automated backups up to 35 days with PITR (restore to new table), or on-demand backups
- Export to S3 without using RCU within the PITR window, import from S3 without using WCU
- Great to rapidly evolve schema
- It is a massively scalable database
- Usecases: Serverless applications development (small documents 100s Kb), distributed serverless cache
-
DocumentDB
- A NOSQL document database that is “MongoDB compatible”
- MongoDB is very popular NOSQL among developers there were open-source licensing issues around using open-source MongoDB , so aws got aorund it by just building their own MongoDB database
- when you want a MongoDB database
-
Amazon KeySpaces
- A fully managed Apache Cassandra database
- Cassandra is an open-source NOSQL key/value database similar to DynamoDB in that is columnar store database but has some additional functionality
- when you want to use Apache Casandra
Relational Database Service
-
Relational Database Services (RDS)
- supports multiple SQL engines
- Relational is synonymous with SQL and Online Transactional Processing (OLTP)
- most commonly used type of database among tech companies and start ups
- RDS supports the following SQL Engines:
- MYSQL - Most popular open source SQL database that was purchased and now owned by Oracle
- MariaDB - When Oracle bought MYSQL. MariaDB made a fork (copy) of MYSQL was made under a different open-source license
- Postgres (PSQL) - Most popular open-source SQL database among developers. Has rich-features over MYSQL but at added complexity
- Oracle - Oracle’s proprietary SQL database. Well used by Enterprise companies. Have to buy a license to use it
- Microsoft SQL Server - Microsoft’s proprietary SQL database. Have to buy license to use it
- Aurora - Fully managed database
- Aurora
- fully managed database,
- database of either MYSQL (5X faster) and PSQL (3X faster) database
- When you want a highly available, durable, scalable and secure relational database for Postgres or MySQL then Aurora is correct fit
- Aurora
- Aurora Serverless - serverless on-demand version of Aurora. - When you want “most” of the benefits of Aurora but can trade to have cold-starts or you don’t have lots of traffic demand
- RDS on VMware - allows you to deploy RDS supported engines to on-premise data center. - datacenter must be using VMware for server virtualization - when you want databases managed by RDS on your own datacenter
Other Database Services
- RedShift
- petabyte-size data-warehouse
- Data warehouses
- are for Online Analytical Procesing (OLAP)
- can be expensive because they are keeping data “hot”
- “HOT” means we can run a very complex query and a large amount of data and get that data very fast
- Usage: when you want to quickly generate analytics or reports from a large amount of data
- ElasticCache
- a managed database of the in-memory and caching open-source databases
- Redis or Memcached
- Usage: when you want to improve the performance of application by adding a caching layer in-front of web-server or database
- Neptune
- a managed graph database
- Data is represented in interconnected nodes
- Usage: when you need to understand the connections between data eg. Mapping Fraud Rings or Social Media Relationships
- Amazon Timestreams
- a fully managed time series database
- Related to Devices that send lot of data that are time-sensitive such as IOT devices
- Usage: When you need to measure how things change over time
- Amazon Quantum Ledger Database
- a fully managed ledger database that provides transparent, immutable and cryptographically variable transaction logs
- Usage: when you need to record history of financial activities that can be trusted
- Database Migration Service
- a database migration service
- Can migrate from:
- On-premise database to AWS
- from two database in different or same AWS accounts using SQL engines
- from a SQL to NOSQL database